Most fields are fertilized with a combination of organic (cow manure) and mineral fertilizers. The idea of using organic manure is practical as well as romantic; you’re completing the nutrient cycle. Cows eat the food you grow, then make the fertilizer that helps make the food they eat. The circle of life!
But manure-based fertilizer has practical uses as well. You can analyze the manure content to calculate the optimal nutrient supply for your crops, meaning that you get information from both ends, so to speak. You can find out if the manure is right for your crops, and you can find out if your cows are getting what they need from your crops.
Additionally, it’s important to analyze your soil to determine the existing nutrient content so that you can adjust fertilizer to supply what may be missing.
How Much Manure?
While there are a few variables to consider in every field, the amount of manure to use depends on the crop type. The USDA offers some guidelines:
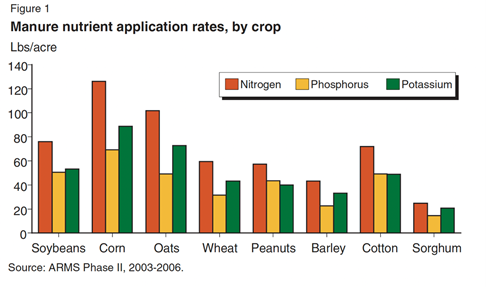
In any field, your crop rotation plays a role in the soil’s nutrient needs for the current season. Your previous crop used certain soil-based nutrients, and it will dictate how much/what formulation you should use on the new crop.
When to Fertilize
Again, every situation is different, but a few best practices should be your guideline. If you fertilize during an extended period of sun and heat without any moisture, you risk significant crop damage.
It’s best not to fertilize in snowy or freezing conditions. Snow will prevent manure from reaching the soil, as will frozen ground. That said, if winter drags on later than usual, some farmers find a little benefit from fertilizing when the ground is “a little frozen.” Not too deep to get bogged down in, and if it’s not too frozen, the nutrients can still penetrate. But in general, it’s not recommended.
Ideally, it won’t be stormy when you fertilize, but rain soon after application is very important for ultimate penetration of the nutrients. That said, too much rain can wash away the nutrients.
So, just make sure the weather is perfect when you apply fertilizer. No big deal!
Equipment Matters
While it’s still too early in most places to start applying your manure, it’s never too early to start prepping your equipment. Make sure your mixer is ready to go and in good working order. Check your tractor, spreader, clean your slurry tank and test your cultivator. Check your overloading auger, and make sure that your manure pit is ready for a load.
In a perfect manure world, you would use a fertilizer system that automatically scans the plants while driving over the field in order to recognize the crops’ nutrient demand so it can spread the exact amount of manure. But many of us have to do it the hard way!
Document your fertilizing activities
Thorough record-keeping is vital to future success. Document the type and amount of fertilizer you used, the nitrogen content, the weather during application, and the specific dates. That way, when you have great success, you can replicate it!



